
In today’s world, where environmental consciousness is at an all-time high. The demand for sustainable packaging innovations like Bioplastic packaging has grown exponentially. Derived from renewable resources such as plant-based materials, they offer a biodegradable and compostable alternative to traditional petroleum-based plastics.
In the food and beverage industry, bioplastic packaging plays a crucial role in preserving freshness and extending shelf life while reducing the environmental impact of packaging waste in the food and beverage sector. In the personal care and cosmetics industry, from toothbrushes and hairbrushes to makeup containers and skincare jars, bioplastics provide a sustainable solution for products that often end up in landfills.
In the pharmaceutical industry, bioplastics are making inroads for reliable packaging material, from pill bottles to medical device components, and bioplastics offer the durability and protection required in the healthcare sector while minimizing environmental impact. Bioplastic packaging stands out as a promising solution as the world continues grappling with plastic pollution and climate change challenges.
Companies in different verticals are choosing bioplastic packaging solutions to demonstrate their commitment to sustainability and attract eco-minded consumers. Let’s explore the exciting world of bioplastic packaging and discover how it has evolved to date.
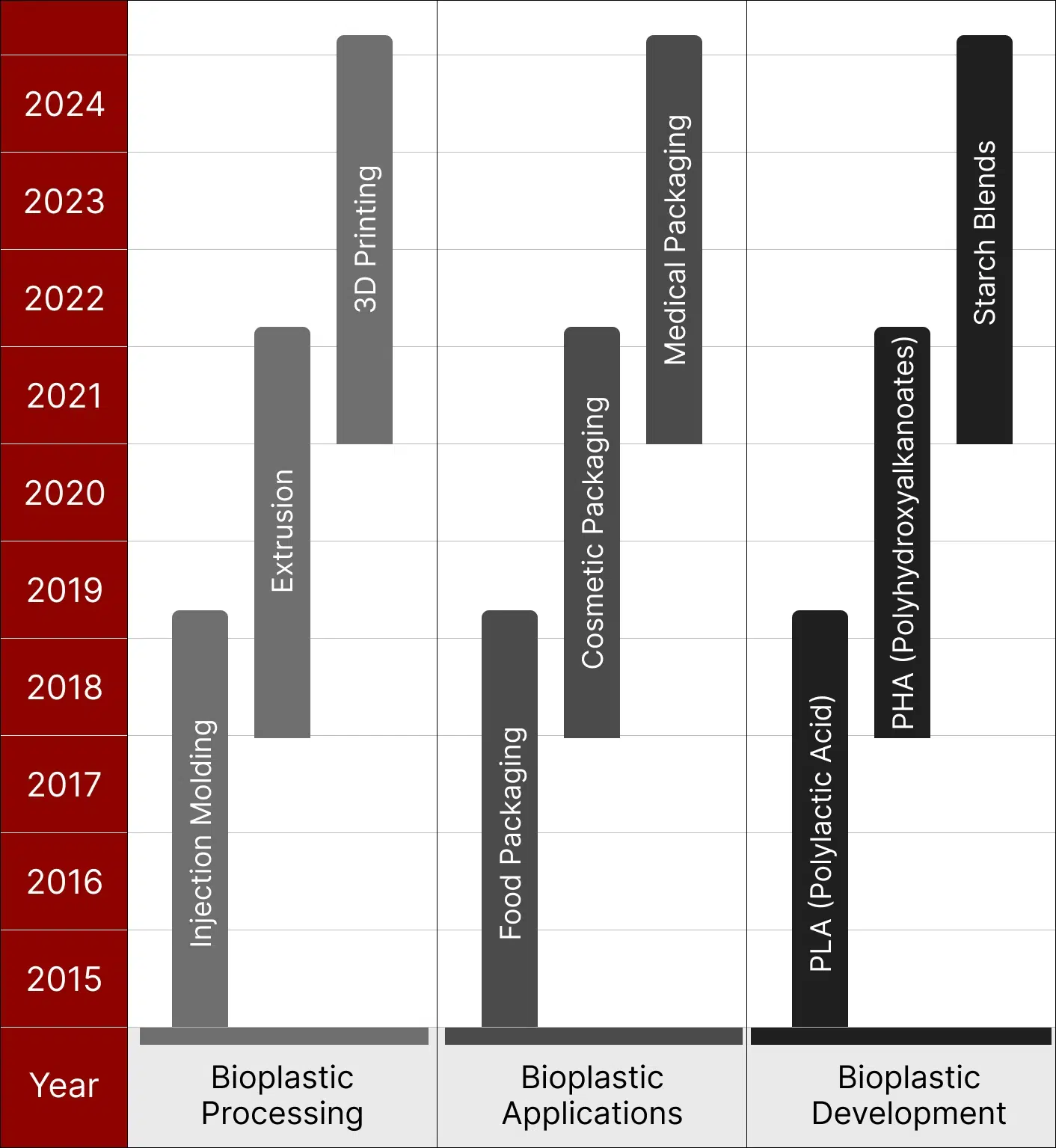
The first bioplastic was discovered by French researcher Maurice Lemoigne in 1926, but it didn’t gain popularity due to the abundance of synthetic plastics at the time. Over the years, bioplastics have evolved from a limited range of materials to a diverse array of options, including polylactide (PLA), polyhydroxyalkanoates (PHA), starch blends, and cellulose-based plastics. The diversification in the raw material has expanded the applications of bioplastics across various industries.
Recently, researchers have focused on enhancing bioplastics’ strength, flexibility, and durability to make them more competitive with conventional plastics. Significant progress has been made in optimizing bioplastic production processes, such as extrusion and injection molding. This has helped improve manufacturing efficiency and cost-effectiveness, making bioplastics more viable for large-scale applications.
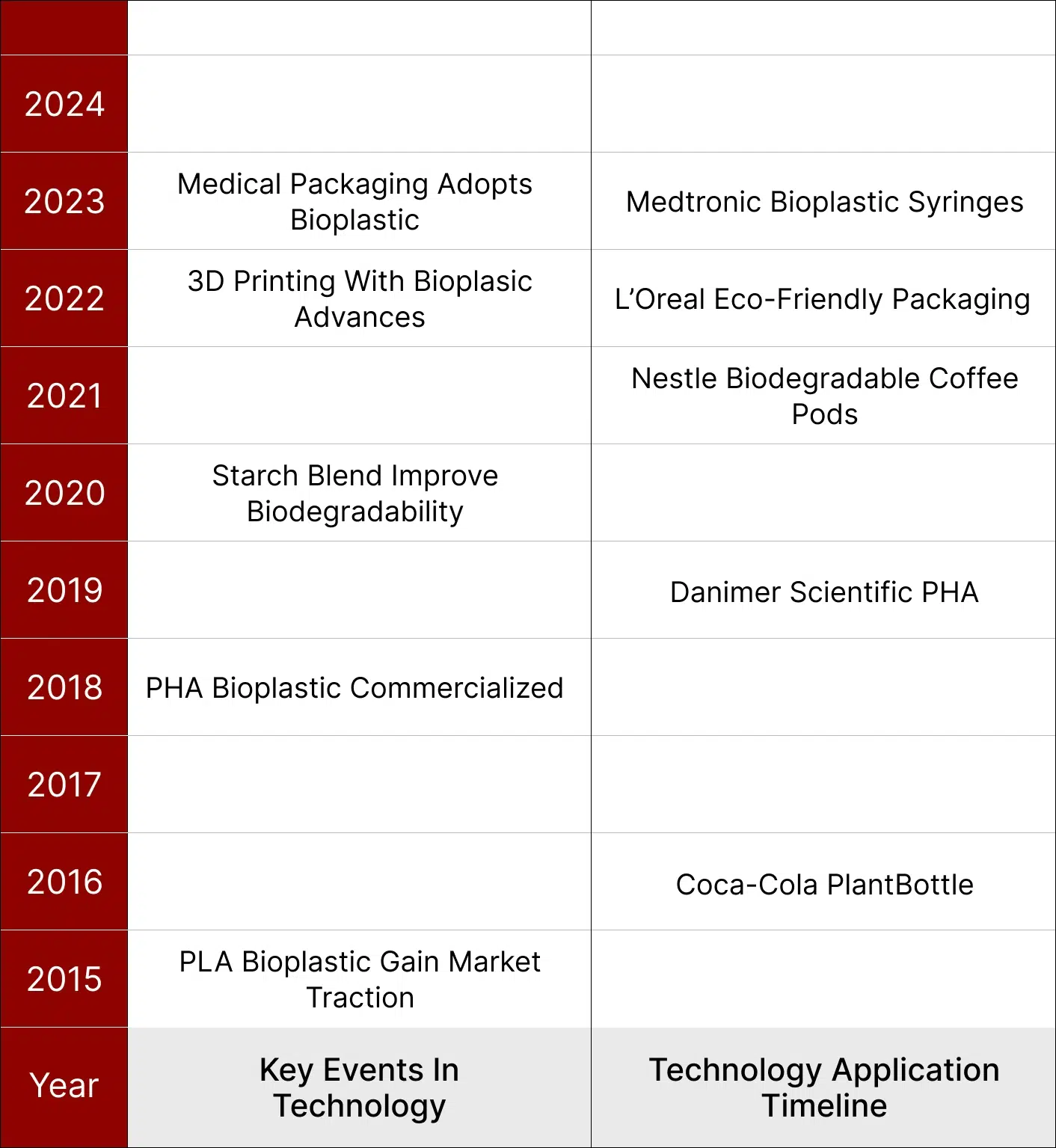
With the technological advancements and cost-effectiveness of bioplastics, their adoption has seen a significant rise across various industries, particularly in packaging. The fact that major brands have started incorporating bioplastics into their products is a promising sign of further innovation and market growth in the field of sustainable packaging. In the next section, let’s explore the market drivers and challenges in bioplastic packaging.
The bioplastic packaging market is growing due to increasing consumer demand for sustainable solutions and government regulations to reduce plastic waste. External factors like climate change awareness, rising fossil material costs, and bioplastics’ technological maturity make them a favourable alternative to conventional plastics. The food and beverage industry, a major user of bioplastic packaging, is driving adoption due to consumer preferences for organic materials. Political support and EU policies like Horizon Europe are crucial for further market development and investment in the bio economy and circular economy.
Bioplastics, derived from renewable resources like corn and sugarcane, face challenges related to land-use competition, energy-intensive production, and higher costs than conventional plastics. Despite being marketed as sustainable, their true environmental benefits remain debated due to factors like greenhouse gas emissions and limited infrastructure degradation. Additionally, bioplastics struggle to match traditional plastics in terms of performance, particularly in packaging, and their reliance on industrial composting facilities— which are not widely available—further complicates their eco-friendly potential, often resulting in landfill waste.
New method to turn banana peels into bioplastic
Researchers from Embrapa Instrumentation and the Federal University of São Carlos have developed bioplastic films from banana peels, which have shown potential as active food packaging.
Method
The simple, eco-friendly process uses water or a dilute acid solution to convert banana peels into films with excellent antioxidant properties and UV protection, outperforming many traditional bioplastics. This innovation addresses the environmental issues of banana peel waste, which generates significant by-products by converting them into valuable bioplastic.
Advantages
Researchers from the Global Institute for Water Security have developed a novel bioplastic pellet designed to address the global water security issue of elevated phosphate levels. This innovative bioplastic made from marine polysaccharides, eggshells, and wheat straw effectively absorbs phosphate from water sources and can be repurposed as agricultural fertilizer.
Advantages
Researchers at the University of Copenhagen have developed a new biodegradable plastic made from barley starch and sugar beet waste fibers. This innovative material decomposes within two months and offers superior strength and water resistance compared to existing bioplastics.
Primary Components
The material’s primary components, amylose and nanocellulose, provide durability and flexibility, making it suitable for applications like food packaging and shopping bags.
Advantages
Researchers from the University of Cordoba and the University of Girona have developed a sustainable bioplastic using avocado pruning waste, offering a potential solution to plastic pollution. Spain’s avocado industry generates significant pruning waste, which researchers have transformed into a composite material by isolating fibers from the waste and combining them with bioplastic.
Advantages
Looking ahead, the future of bioplastics technology is promising, with ongoing research focused on developing even more advanced materials and production methods. Innovations in areas like biodegradable nanoparticles for drug delivery and tissue engineering are expected to drive further advancements in the field.
One of the most notable developments is the introduction of new materials such as polylactic acid (PLA), polyhydroxyalkanoates (PHA), and bio-based polybutylene succinate (Bio PBS), which offer enhanced properties like biodegradability, breathability, and increased material strength. Additionally, polyethylene furanoate (PEF) has emerged as a promising alternative, providing superior barrier properties compared to traditional polymers and being easily mechanically recycled.
Wissen Research analyses that the global bioplastic packaging market is estimated at ~USD 11 billion in 2023 and is projected to reach ~USD 30.2 billion by 2030. The market is expected to grow at a CAGR of ~10% during the forecast period, 2024-2030. If you are interested in in-depth bioplastic packaging market insights, we’ve got a comprehensive report for you. Get in touch with our subject matter experts today!