Subscribe our newsletter
Please Subscribe our news letter and get update.
The COVID-19 pandemic has highlighted the importance of resilient supply chains and human-machine collaboration at workplace. Regulations against social distancing and complete or partial shutdowns forced businesses like factories and offices to run on the bare minimum of onsite employees.
Manufacturers were constantly under pressure to adapt to the changing markets due to labour shortages, supply chain interruptions, and other production issues. Demands for mass customisation, high-quality standards, quick product cycles, and product variety are at an all-time high. It takes a combination of human talent and creativity with robotic speed and strength to overcome these persistent obstacles.
Manufacturers, hence, should use collaborative robots – or cobots that can shorten production cycles and reduce human contact when necessary to bring together human creativity and robotic precision.
Why is the future of manufacturing around cobots? How do they promote manufacturing resilience? Continue reading this blog to learn more.
Robots with the capability to work collaboratively with humans are known as “Cobots.” The idea behind cobots is that they work alongside humans to help speed up processes or do mundane activities. The goal of this collaboration is to securely augment human abilities.
The market for collaborative robots was worth $701.56 million in 2021. By 2030, it is expected to grow at a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 15.2% to $2506.90 million.
Top Cobot Manufacturing Companies: Universal Robots, Kuka, Rethink Robotics, TechMan Robot, ABB.
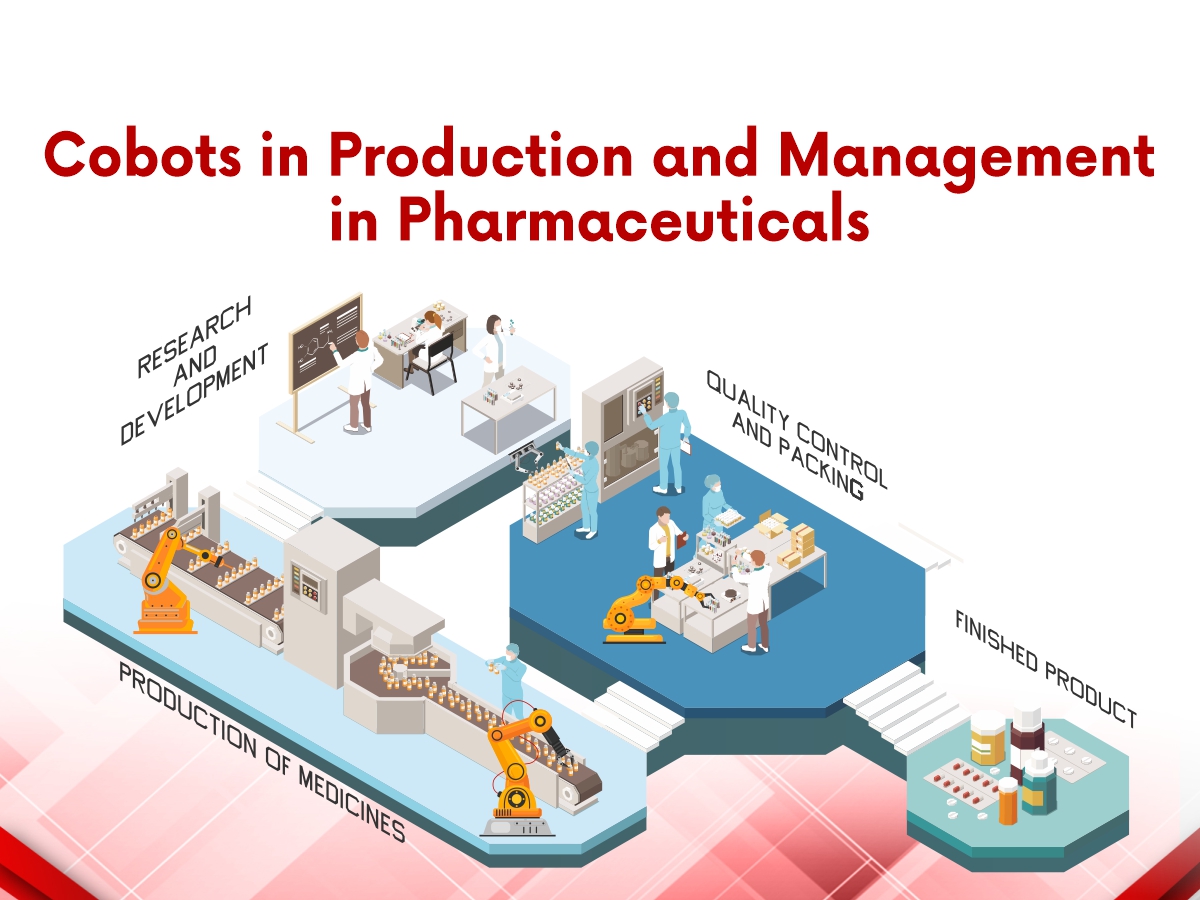
Pharmaceutical manufacturing is characterised by mass production, accuracy, and sterility. Pharma can benefit from these Collaborative Robotic arms (Cobot) to enhance drug production, quality control, and efficiency in pharmaceutical research.
Once a cobot has been programmed, repetitive operations can be carried out with little error. Cobots are ideal for preventing contamination in sterile surroundings. Many cobots can operate efficiently without breaks or maintenance. Because of this, most sectors see a cobot’s return on investment within a year.
Cobots Increase Manufacturing Efficiency
Cobots, or collaborative robots, are made to safely operate with humans in laborious, monotonous, and hazardous conditions. Cobots function alongside human labour in a shared workspace, in contrast to traditional industrial robots that operate in guarded premises to avoid close proximity with humans.
Cobot movements are guided by robot arms and other manipulators that are computer-controlled and under human supervision. As a result, cobots enable productive human-machine collaboration at work.
The use of collaborative robots is essential in automating the pharmaceutical sector, for the following reasons.
Cobots are equipped with gripper technology that enables them to lift and move objects of different sizes, shapes, and weights. This not only lessens the burden on a person’s body but also makes it possible to package and palletize a greater number of things. This can involve picking things off a conveyor belt and placing them in a work area or organising items for future processing.
Workers find inspection challenging because it requires constant, intense concentration. For pharmacists, an inspection error might have fatal implications. Due to their high level of consistency, cobots can be a blessing in this situation. The key benefit, in this case, is that cobots maintain focus longer than humans do, which is a crucial quality for quality assessment. For instance, cobots can check that blister packs are fully packed or look for defects in them.
Cobots can be used for large-scale dispensing, significantly speeding up the ordering and fulfilment of prescriptions. Cobots can be set up to recognise various sorts of drugs as well as carry out repetitive tasks. They may be programmed to read barcodes and identify the shape, size, and weight of pills. They are capable of choosing and dispensing the right drugs as they are equipped with advanced gripping mechanisms.
They may also be able to monitor stock levels and provide instructions or signals to acquire more when necessary.
Cobots have robotic arms that are very flexible and can perform a variety of jobs. They can be programmed to operate independently or in collaboration with people.
Assembly applications range from fitting tiny items to assembling large parts. Software can be developed and used to instruct cobots to build medical supplies like implants and prosthetics. There are also smaller robots with particular pick-and-place capabilities that allow for precise, quick assembly of small parts like glass vials with covers and tube coils with end fittings.
The storage of pharmaceutical supplies must be done properly and safely. Any mistake with supplies that are not properly stored can have serious repercussions. The 3D vision calibration of cobots enables them to help with tasks like tray stacking. A cobot can determine an object’s 3D shape from a picture. This enables it to lift and stack trays. Also, it can add and remove items from trays.
Human-robot collaboration (Cobot) is a viable strategy to increase production while lowering costs since it combines a cobot’s strength and precision with a human’s capacity to assess, respond, and strategize.
The bottom line is that the use of cobots enables robots and people to coexist in the same workspace, thus making human workers more efficient and not replacing them!
Thus, the cobot market is expected to grow substantially in the coming years.
Please Subscribe our news letter and get update.
© Copyright 2024 – Wissen Research All Rights Reserved.