Subscribe our newsletter
Please Subscribe our news letter and get update.

A brand name or logo is a representative of the product or services that can help customers recognize the source of quality and exclusivity in the market, so it is very important to choose a unique name for the company.
A trademark search looks up the availability of your desired trademark by searching public and/or private databases.
It is not required that you look for trademarks. However, you can subsequently find out that someone else already holds a conflicting trademark if you begin using a trademark or pay to file for registration of a trademark without first conducting a search. You might be held accountable for trademark infringement if this occurs. You will not be able to obtain a trademark registration if the other party began using their mark before you did. Furthermore, you will need to modify all of your branding and select a new trademark. This can be frustrating and very expensive. You should run a trademark search on a search engine before you request to file your trademark with the government trademark office.
These costly and dangerous errors can be avoided with a trademark search. You will be able to apply for a trademark with confidence if you take the extra time and financial investment to conduct a clearance search.
The following are some of the reasons for trademark clearance searches:
Trademark searches primarily fall into two categories: “Preliminary trademark search” and “Comprehensive trademark search”.
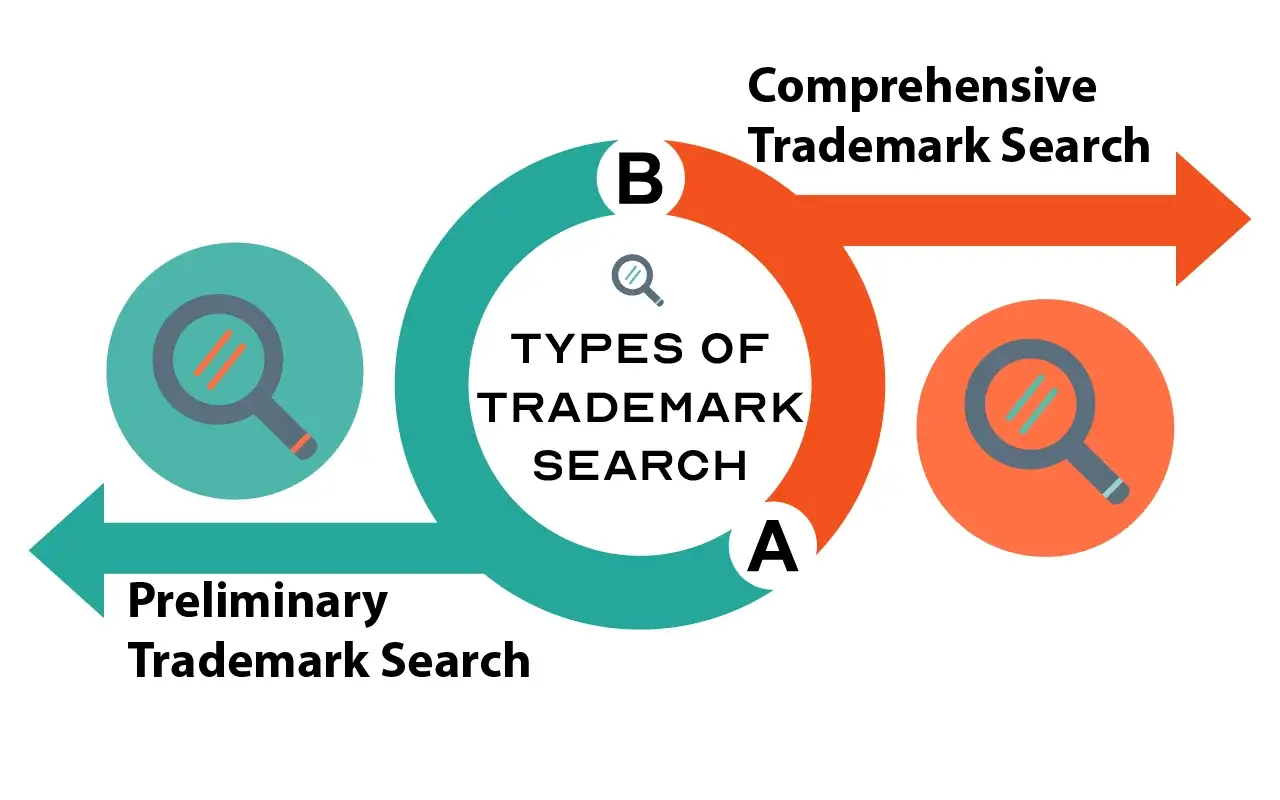
Preliminary trademark search: Another name for a preliminary trademark search is an “exact match” or “knockout” search. This kind of search finds names that are exact matches as well as names that could be one or more letters different from the name you want for your trademark.
Comprehensive Trademark Search: Several public and private databases containing corporate names, domain names, state trademarks, news announcements, business publications, and other information are examined in a comprehensive trademark search. This kind of search finds trademarks that might not be the same, but it might hinder your registration attempts for other reasons.
If there are any other registered marks that are “confusingly similar,” indicating they are likely to cause confusion in the marketplace but not exactly the same, a Comprehensive Search can reveal this information to you. Your application will be rejected if it contains “confusingly similar” trademarks.
Even if someone hasn’t submitted an official application for trademark registration, a Comprehensive Search can still reveal whether they are the owner of trademark rights in a name that is similar to yours. One nation that is “first to use” is the United States. Even if they did not register the name with the federal government, the rights of the person who began using the trademark before you will nullify your rights to any “confusingly similar” name.
Only a Comprehensive Trademark clearance Search can reveal these unregistered marks. Unregistered trademarks put new applicants at significant silent risk. The owner of the unregistered trademark may file a petition to have your registration cancelled even after you have successfully registered your desired trademark. They just need to demonstrate that they sold goods under the name before you in order to succeed.
In the worst situation, you can even find yourself liable for infringement damages equal to three times your earnings from using the trademark while being aware of the other brand owner.
A trademark search must be performed by the applicant for a registered trademark. The proposed trademark’s excessive similarity to an already-registered trademark is the most frequent cause of trademark application rejections.
In addition, a trademark search should be carried out by anyone intending to use a trademark, even if it has not been registered for commercial use. As intellectual property, trademarks are protected. If someone uses a trademark that is too close to or a copy of a registered trademark, they may be sued.
Performing a comprehensive trademark clearance search can guarantee that a business is granted approval for trademark registration and safeguard it against infringement on the intellectual property of other businesses.
Wissen Research has a team of trademark experts who have over 10 years of experience and have conducted over 5000 different types of searches worldwide.
Also, Wissen Research always includes variations such as identical, phonetic similarity, vowel and consonant similarity, and other similarities in the report, as well as using paid and national PTO databases to cover all potential results in the report.
We strongly focus on the goods and services for the search by marking all the combinations to avoid any identical and phonetically similar trademark infringement results.
We offer specialized Internet searches to locate NFT or crypto-property trademark results that are doing business without registering as a trademark. We search the trademark name or design under the goods and services (the goods and services for which most trademark applications are filed for NFT trademarks) mentioned below.
According to WIPO, the category of goods for which these applications have been filed mainly relates to:
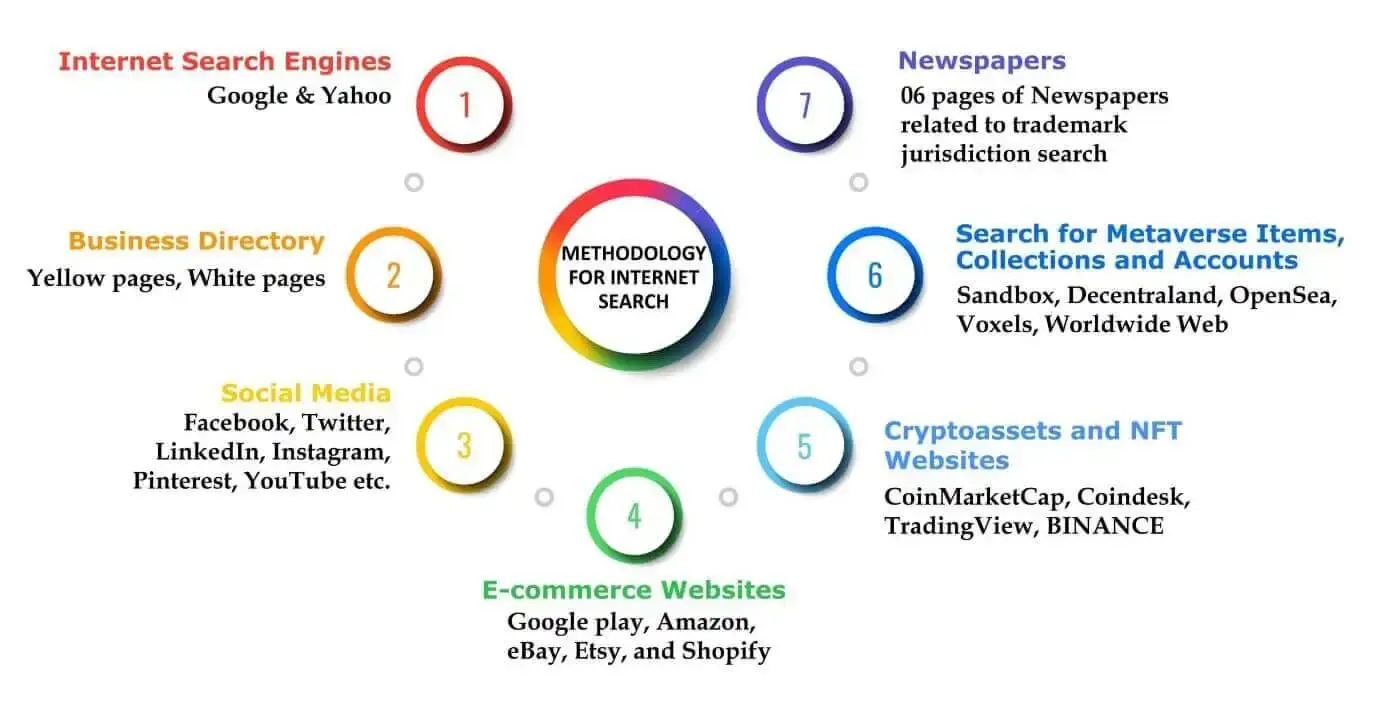
Additionally, we use the below-mentioned methodology of internet search to cover the potential results of NFT or crypto-property trademarks.
Please Subscribe our news letter and get update.
© Copyright 2024 – Wissen Research All Rights Reserved.