Certification trademarks serve as vital indicators in consumer landscapes, signifying adherence to specific quality, safety, or ethical standards. These visual symbols guide decisions and foster trust by ensuring products or services meet stringent criteria set by certifying bodies.
Diverse Range of Certification Marks
Certification trademarks span various attributes:
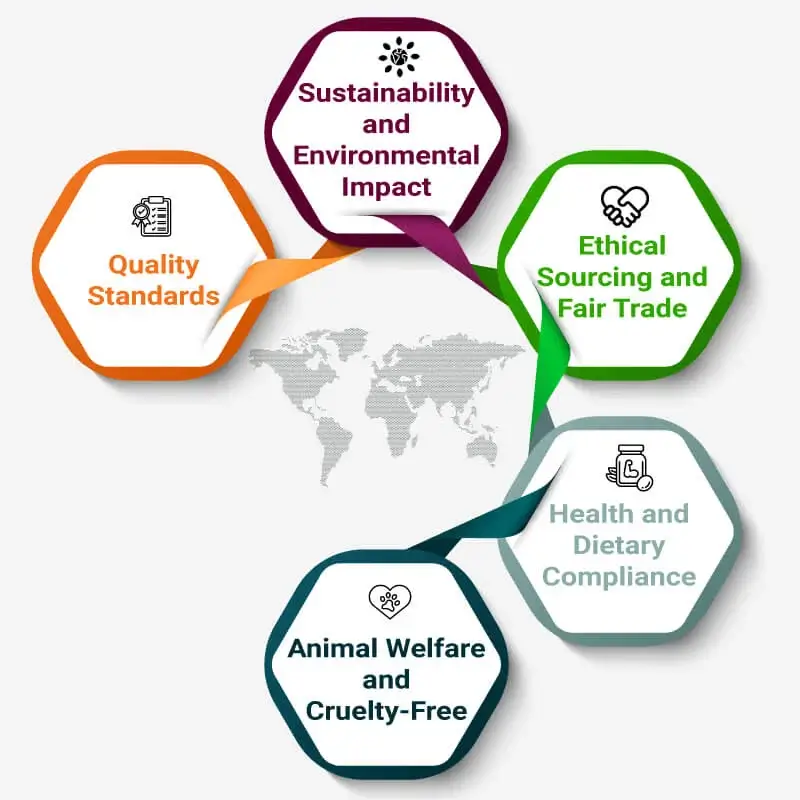
Consumer Benefits
Certification trademarks offer consumers:
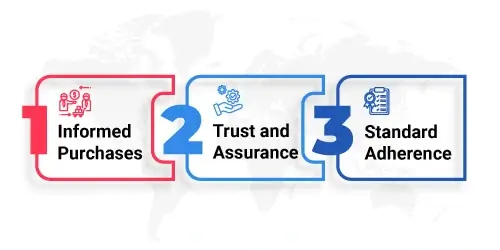
Recognition and Utilization of Certification Marks
These marks come in various forms – labels, symbols, or seals – prominently featured on product packaging, websites, or promotional materials. Understanding these symbols empowers consumers to make conscious choices in line with their beliefs and priorities.
Role of Trademark Services:
Trademark Search: Ensures new certification marks are unique and non-conflicting, preserving their distinctiveness and preventing consumer confusion.
Trademark Monitoring: Protects certification trademarks by monitoring for misuse or infringement, maintaining their authenticity and guiding consumer decisions.
These services reinforce the integrity and exclusivity of certification marks, upholding their credibility and fostering consumer confidence in products or services bearing these symbols.
Types of Certification Trademarks and Examples
Certification trademarks serve as affirmations of a product’s adherence to specific standards, instilling confidence in its quality, safety, or ethical considerations. These symbols, diverse across industries, represent distinct criteria and values:
Logo:
Examples: Organic Valley – Credit :https://organicvalleyindia.com/butter.php
Logo:Fair Trade Certified Symbol, Credit : https://www.fairtrade.net/about/fairtrade-marks
Example: Divine chocolate Credit:https://www.amazon.com/Dark-Chocolate-Coins-Gelt-Pack/dp/B08KYHYYY2
#Energy Efficiency Certification (Energy Star): Indicates products meeting energy efficiency standards.
Logo:Energy Star label Credit : https://www.energystar.gov/productfinder
Example: Carrier, Credit :https://cmiestore.com/split-inverter-ac/18k-5-star-indus-dxi
#ISO Certification: International standards ensuring quality management (ISO 9001) and environmental management (ISO 14001) in various industries.
Logo:
Example: dnv gl, Credit :https://www.dnv.com/assurance/Management-Systems/Use-of-certification-marks.html
#LEED Certification: For buildings and construction projects, ensuring sustainable and environmentally friendly designs, construction, and operation.
Example: An example of a LEED-certified building is the Bank of America Tower at One Bryant Park in New York City. This skyscraper was awarded LEED Platinum certification, the highest level of certification in the LEED rating syst
#Kosher Certification: Certifies compliance with Jewish dietary laws.
logo:
Example: Chicago Rabbinical Council (cRc) – Credit:https://crckosher.org/
#Cruelty-Free Certification: Verifies that cosmetics or personal care items were not tested on animals.
Logo:
Example: DOT & KEY
#Ethical or Religious-based Certifications: Certifications aligning with specific ethical or religious guidelines.
logo: #Halal certification
#Halal symbols
Credit : https://www.skymoonworld.com/halal/
Credit:https://www.flipkart.com/nestle-instant-lemon-flavour-iced-tea-pouch/p/itm77fb7c6e18223
Certification trademarks are essential tools in consumer decision-making, enabling individuals to align purchases with ethical considerations, dietary needs, and value systems. These symbols stand as testaments to adherence to set standards, promoting transparency and trust within an increasingly conscientious market landscape.
Authored by – Nitesh Chouhan
Edited by : Guniyal