In the ever-evolving landscape of technology, innovation has seeped into every aspect of our lives, including the way we package and consume products.
Smart packaging provides numerous advantages for both the distribution of products and manufacturing operations. Utilizing advanced technologies can enhance traceability, lower expenses, boost efficiency, and elevate product quality across various sectors, including food production. Moreover, in manufacturing settings, it has the potential to automate and streamline processes, ultimately enhancing productivity and efficiency levels.
Smart packaging solutions are reshaping the way products are packaged, delivered, and experienced by consumers. The integration of technology not only enhances the functionality of packaging but also opens up new possibilities for brand engagement and sustainability. As industries continue to embrace these innovations, smart packaging is set to become an integral part of our daily lives, introducing a new era of convenience, transparency, and environmental consciousness.
In this blog, we will cover what is smart packaging, focusing on its two main categories– Active and Intelligent Packaging, their benefits and future outlook. Discover our comprehensive range of technology-driven solutions by visiting our Technology Landscape service page.
Now, let’s start with the basics first.
A smart packaging solution elevates traditional packaging through the integration of advanced technologies, offering features like RFID tags, NFC communication, and temperature sensors. These innovations ensure product authenticity, traceability, and safety while providing engaging experiences for consumers. From monitoring freshness to detecting tampering, smart packaging meets the evolving demands of modern consumers and businesses, promising a smarter, more connected future.
Now, let’s dive deeper into both of these categories.
Active packaging refers to the incorporation of substances or technologies within the packaging material itself to actively interact with the product or its environment. The primary goal is to extend the shelf life of the product, enhance safety, and maintain optimal quality. Here are some key examples of active packaging:
A. Oxygen Scavengers:
Active packaging can include oxygen scavengers that absorb or reduce the presence of oxygen within the packaging. This is particularly crucial for products sensitive to oxidation, such as food and pharmaceuticals.
B. Moisture Absorbers:
Products vulnerable to moisture, like electronics or certain medications, can benefit from active packaging containing moisture-absorbing materials. This helps prevent degradation and ensures the integrity of the product.
C. Ethylene Absorbers:
Fruit and vegetable packaging often includes active components that absorb ethylene, a natural gas released by certain fruits, to extend the freshness of the produce.
D. Antimicrobial Agents:
Active packaging with antimicrobial properties can inhibit the growth of bacteria and fungi, preserving the quality and safety of perishable goods.
Intelligent packaging goes beyond the physical protection of products, incorporating technologies that provide valuable information about the condition and history of the packaged item. This real-time data can be accessed by consumers, retailers, and manufacturers. Here are some examples of intelligent packaging:
A. RFID (Radio-Frequency Identification):
RFID tags embedded in packaging enable tracking and tracing of products throughout the supply chain. This not only enhances inventory management but also helps prevent counterfeiting and improves overall transparency.
B. NFC (Near Field Communication):
NFC technology allows for communication between the packaging and mobile devices. Consumers can access detailed information about the product, including its origin, expiration date, and usage instructions, by simply tapping their smartphones on the packaging.
C. QR Codes and Augmented Reality:
QR codes on packaging can lead consumers to interactive content, while augmented reality (AR) applications can provide immersive experiences, such as virtual tours of production facilities or engaging product-related games.
D. Temperature and Time Indicators:
Smart packaging can incorporate indicators that change color or provide alerts when a product has been exposed to unfavorable conditions, such as excessive heat or extended storage time.
Now let’s learn about the applications of Smart Packaging in different industries.
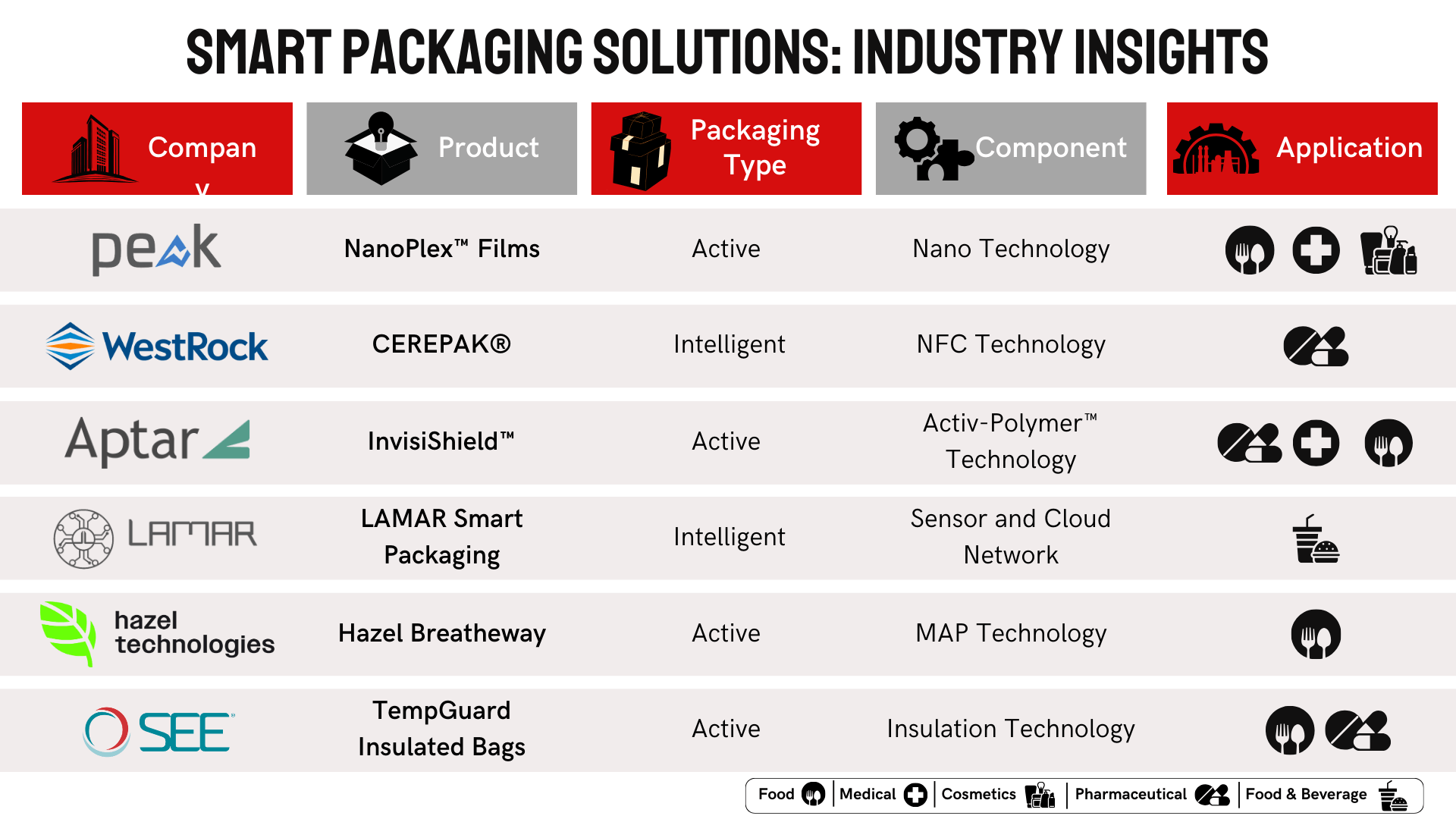
Smart packaging revolutionizes industries, offering dynamic solutions that enhance product experiences and supply chain efficiency. The benefits include:
The adoption of smart packaging brings forth a multitude of benefits, ranging from improved product safety to enhanced consumer engagement. The integration of active and intelligent packaging leads to:
As technology continues to advance, the possibilities for smart packaging are limitless. From personalized nutrition recommendations to blockchain-enabled traceability, the future of packaging holds exciting prospects for both consumers and industries alike. As we unwrap the potential of smart packaging, we pave the way for a more sustainable, efficient, and interconnected future.
Staying ahead of the curve in this dynamic field requires a keen understanding of the latest technological trends and innovations. Explore the future of Smart Packaging Solutions with Wissen Research’s expert Technology research analysis. We guide businesses in staying ahead through strategic technological insights. Visit our Technology Landscape service page to shape your success in the dynamic field of smart packaging solutions.
Authored By :- Guniyal