Subscribe our newsletter
Please Subscribe our news letter and get update.
[newsletter]

About NPC
History: Niemann-Pick Disease Type C (NPC) was first described by German pathologists Albert Niemann and Ludwig Pick in the early 20th century. They independently reported cases with similar clinical and pathological features. However, the underlying genetic and molecular basis of the disease wasn’t fully elucidated until much later. Over the years, advancements in genetic research have provided insights into the autosomal recessive inheritance pattern and the identification of causative genes (NPC1 and NPC2). This has led to a better understanding of the disease’s pathophysiology and potential treatment strategies.
Clinical Characteristics: Niemann-Pick Disease Type C (NPC) is a rare and slowly progressive lysosomal disorder that presents with a range of age-dependent clinical manifestations. In the perinatal and infantile periods, patients exhibit visceral symptoms such as hepatosplenomegaly, jaundice, and, in some cases, pulmonary issues. As affected individuals enter late infancy and beyond, the disease’s presentation shifts to predominantly neurological symptoms. Early symptoms may include hypotonia and developmental delay, followed by ataxia, dysarthria, dysphagia, and, in some cases, epileptic seizures, dystonia, and gelastic cataplexy. Over time, progressive dementia becomes apparent.
In older teenagers and young adults, early-onset dementia or psychiatric manifestations might be more prominent, overshadowing neurological symptoms. However, careful examination typically reveals characteristic neurological signs. The disease’s manifestations can vary widely, and diagnosis can be challenging, particularly due to the overlap with other disorders.
Diagnosis and Testing: The diagnosis of NPC is established through molecular genetic testing, specifically identifying biallelic pathogenic variants in either the NPC1 or NPC2 gene. Oxysterol testing has become a robust screening and diagnostic tool. Genetic testing approaches can include multigene panels or comprehensive genomic testing, depending on the patient’s clinical presentation. The distinctive clinical findings, family history, and molecular testing contribute to the diagnosis.
Treatment: As of now, there is no cure for Niemann-Pick Disease Type C. Treatment primarily focuses on managing the disease’s manifestations and providing supportive care across various disciplines:
Symptomatic Treatment: Neurology, physical therapy, occupational therapy, speech therapy, and nutrition specialists collaborate to provide supportive therapy. This multidisciplinary approach aims to address mobility issues, speech and language difficulties, feeding problems, and spasticity.
Miglustat Treatment: Miglustat is a medication approved for managing neurological symptoms of NPC in some countries (not including the United States). Clinical studies have shown that miglustat can extend survival by approximately five years from diagnosis or around ten years from the onset of neurological symptoms. It’s important to note that this treatment doesn’t offer a cure but can slow down disease progression.
Surveillance: Regular follow-up by a team of specialists helps monitor disease progression and manage supportive care effectively. Psychosocial support is integral to identify new disease manifestations, assess miglustat compliance and side effects, and adjust therapy as needed.
Avoidance of Aggravating Factors: Certain medications and substances, such as drugs that exacerbate seizures or worsen ataxia, should be avoided. Alcohol and specific drugs that interact with antiepileptic medications should also be avoided.
Genetic Counseling: NPC follows an autosomal recessive inheritance pattern. Genetic counseling is crucial for families with affected individuals. Carrier testing can be conducted for at-risk relatives, and prenatal testing and preimplantation genetic testing are options for pregnancies at increased risk.
In conclusion, Niemann-Pick Disease Type C is a complex disorder with variable clinical presentations that evolve with age. While no cure currently exists, a multidisciplinary approach to treatment and the use of miglustat can help manage symptoms and extend survival. Genetic counseling plays a vital role in understanding inheritance patterns and making informed decisions for at-risk relatives. Ongoing research into potential treatments and interventions continues to offer hope for improving the quality of life for individuals with NPC.
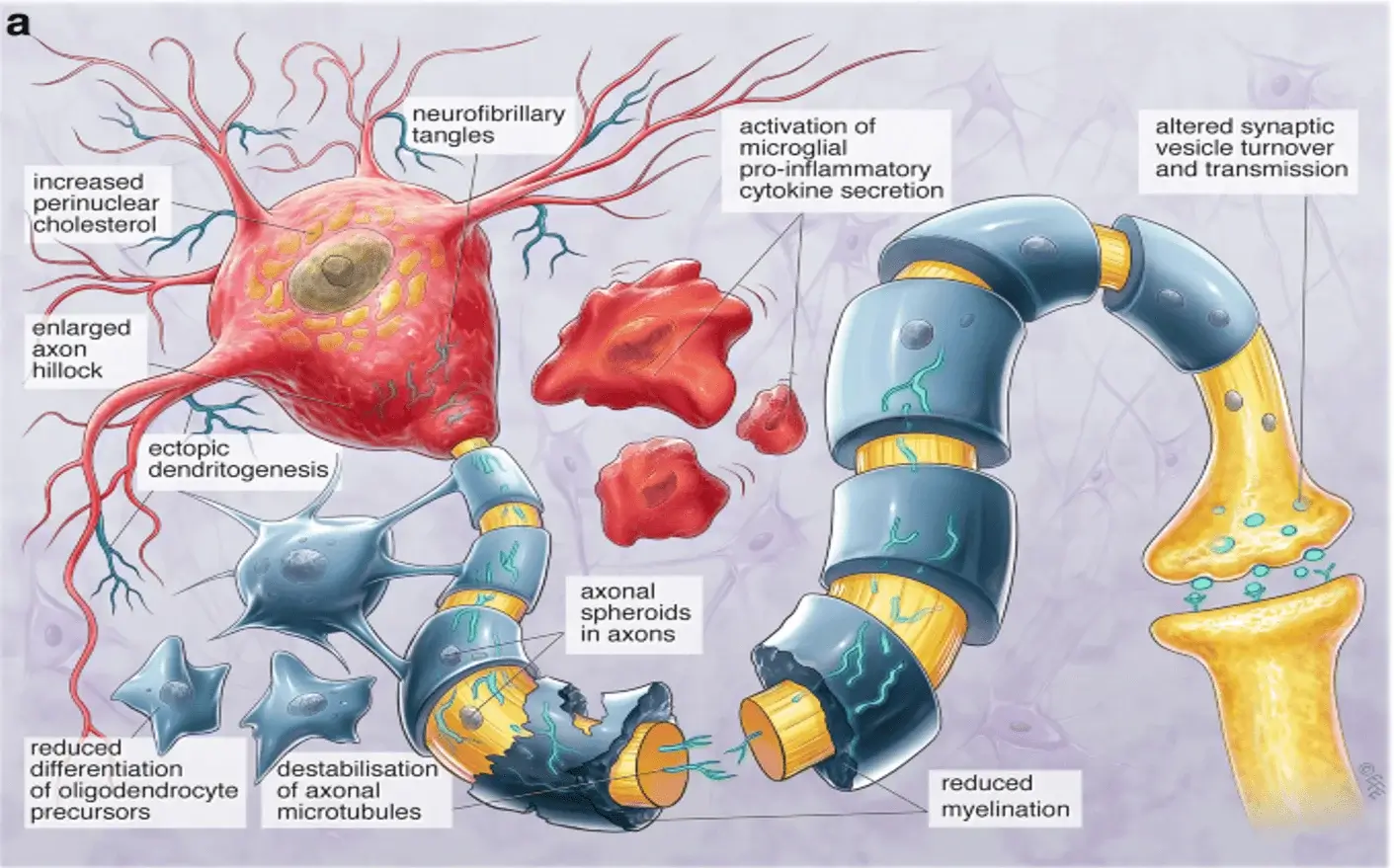
Figure 1: Psychiatric and cognitive symptoms
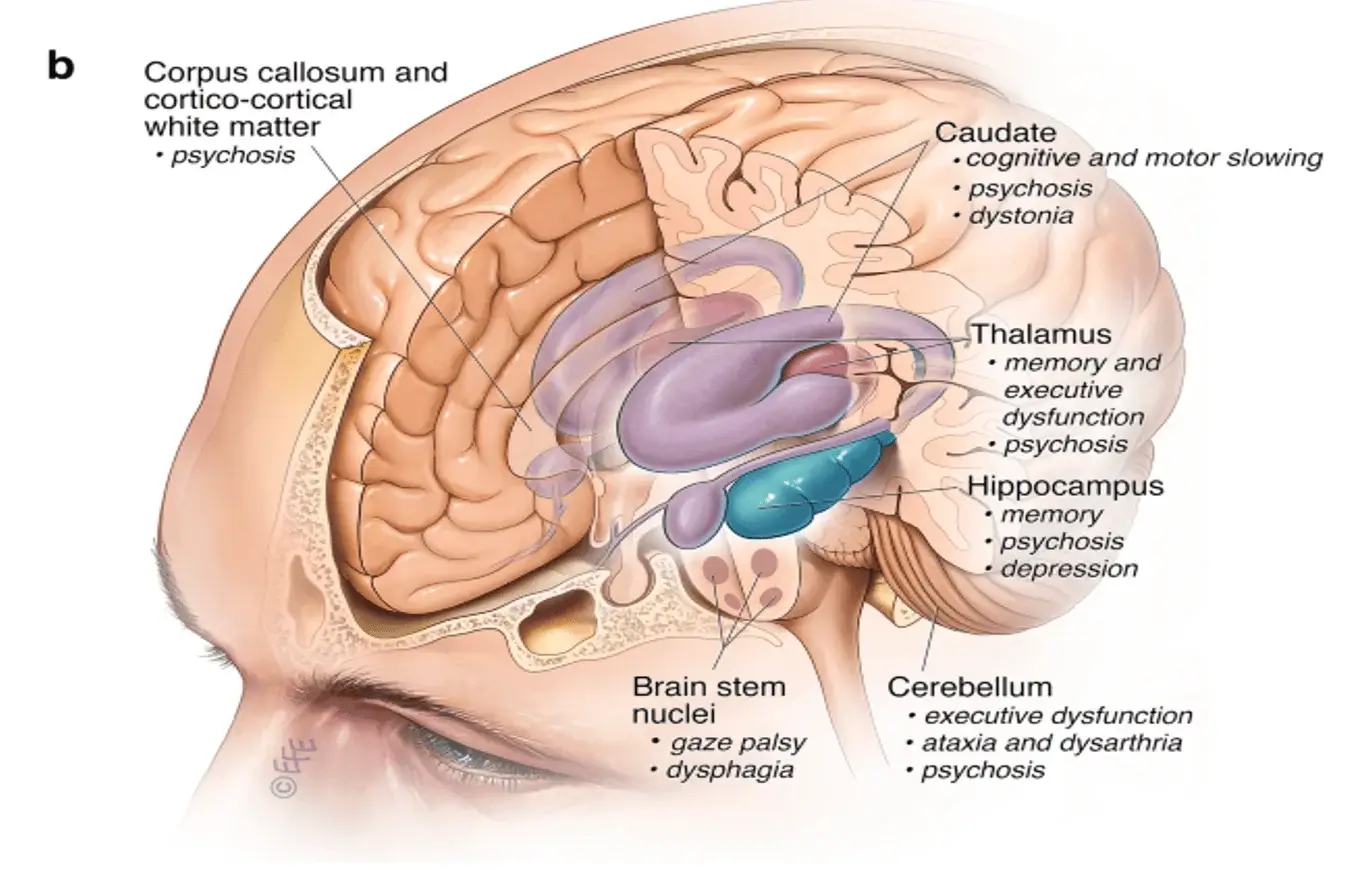 credit by (https://link.springer.com/article/10.1007/s40263-018-0599-0)
credit by (https://link.springer.com/article/10.1007/s40263-018-0599-0)
To gain a comprehensive grasp of the competitive landscape in the realm of Niemann-Pick Disease Type C (NPC) over the near to medium-long term, acquiring knowledge about the ongoing research and developmental pipeline becomes essential in strategically positioning a treatment within the market.
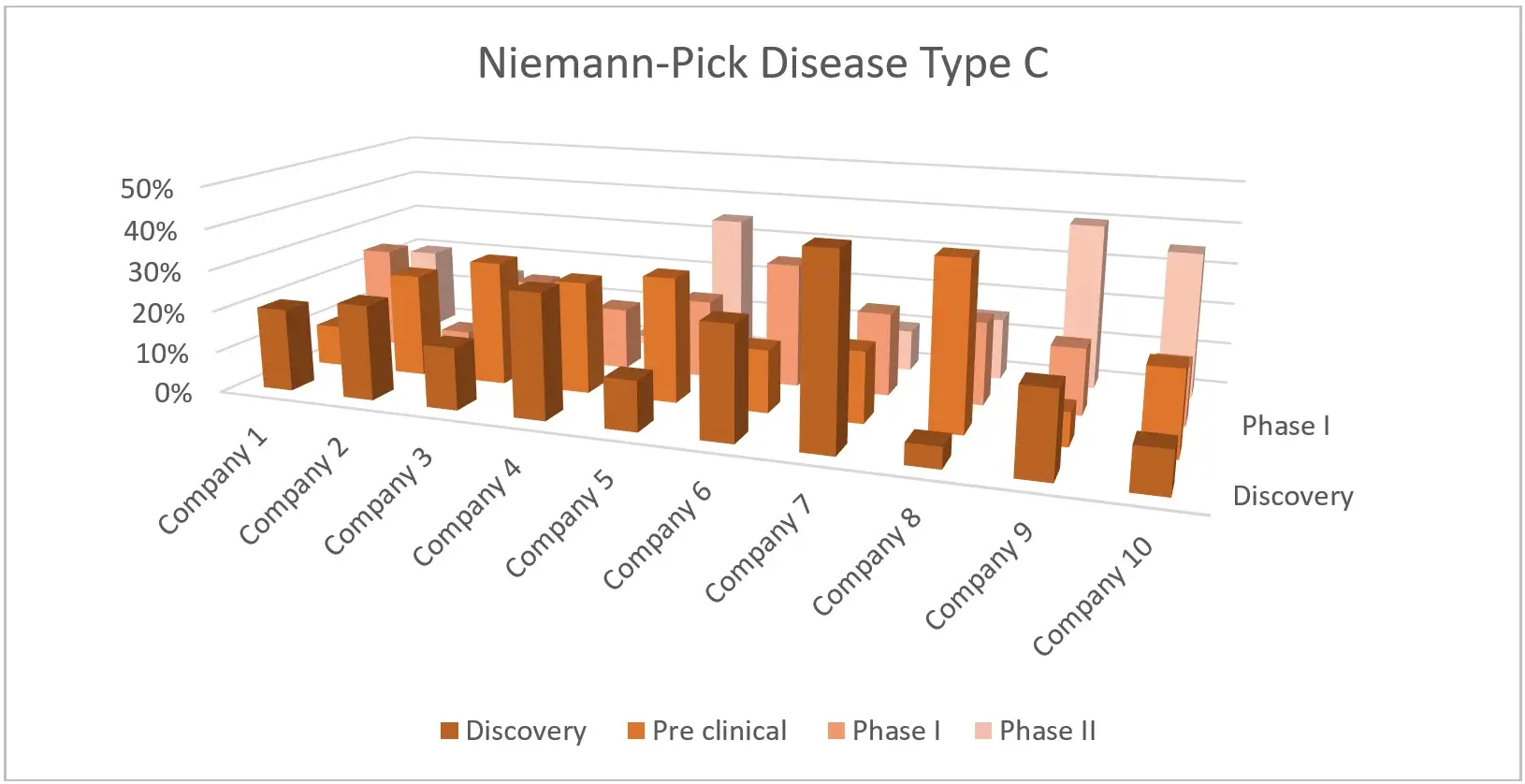 Market Landscape: Niemann- Pick Disease Type C (NPC): Example Illustration: Distribution by Pipeline Candidates
Market Landscape: Niemann- Pick Disease Type C (NPC): Example Illustration: Distribution by Pipeline Candidates
Depicted here is the active involvement of stakeholders in influencing treatments for Niemann-Pick Disease Type C (NPC), including insights into financial considerations, product offerings, and recent progressions.
Examining patents provides invaluable insights into revolutionary breakthroughs and emerging technologies in the field of Niemann-Pick Disease Type C (NPC), enhancing our understanding of new approaches for cutting-edge therapies.
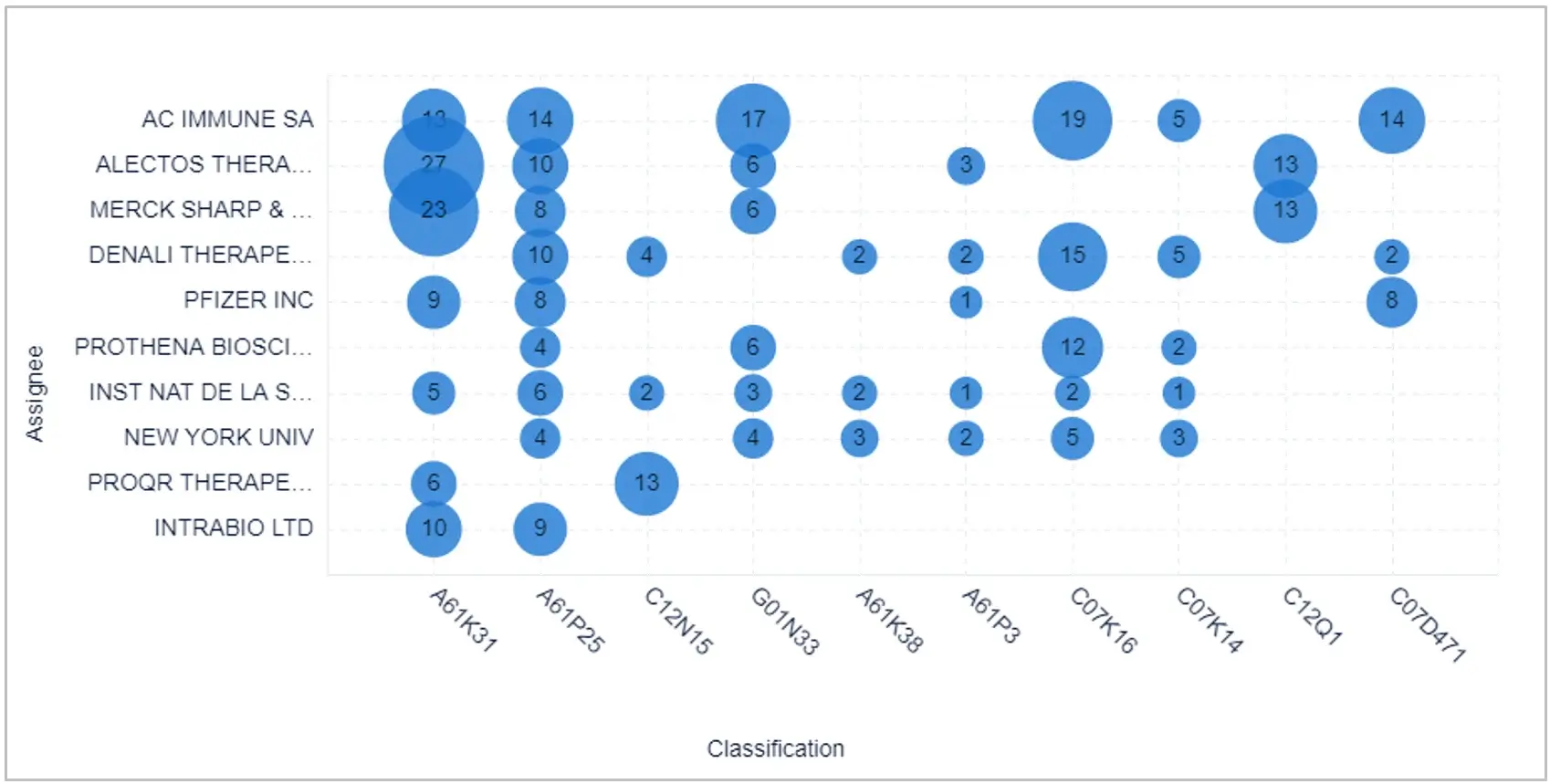
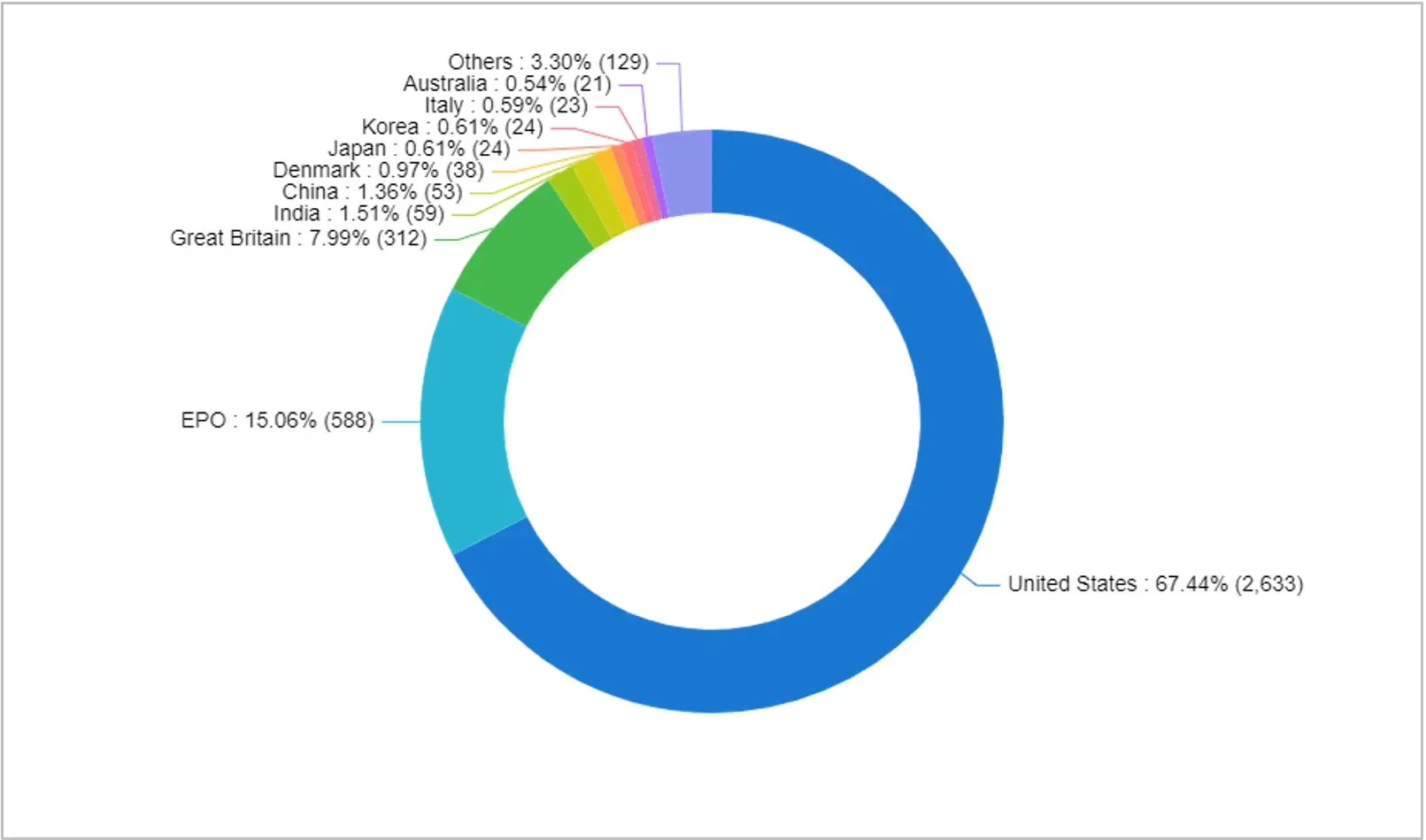
On the basis of current assignees:
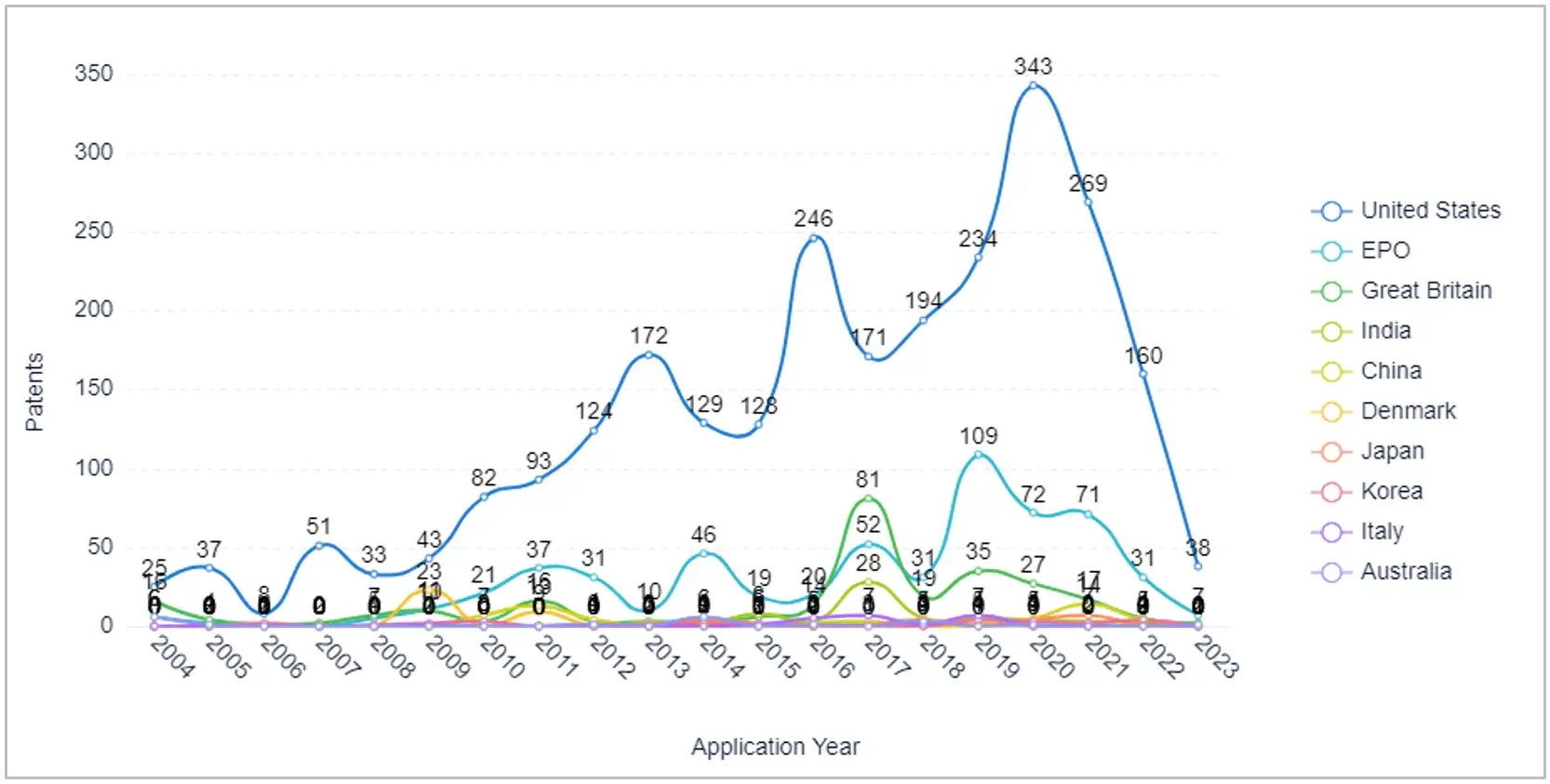
On the basis of the application year in top countries:
Data about new Entrants:
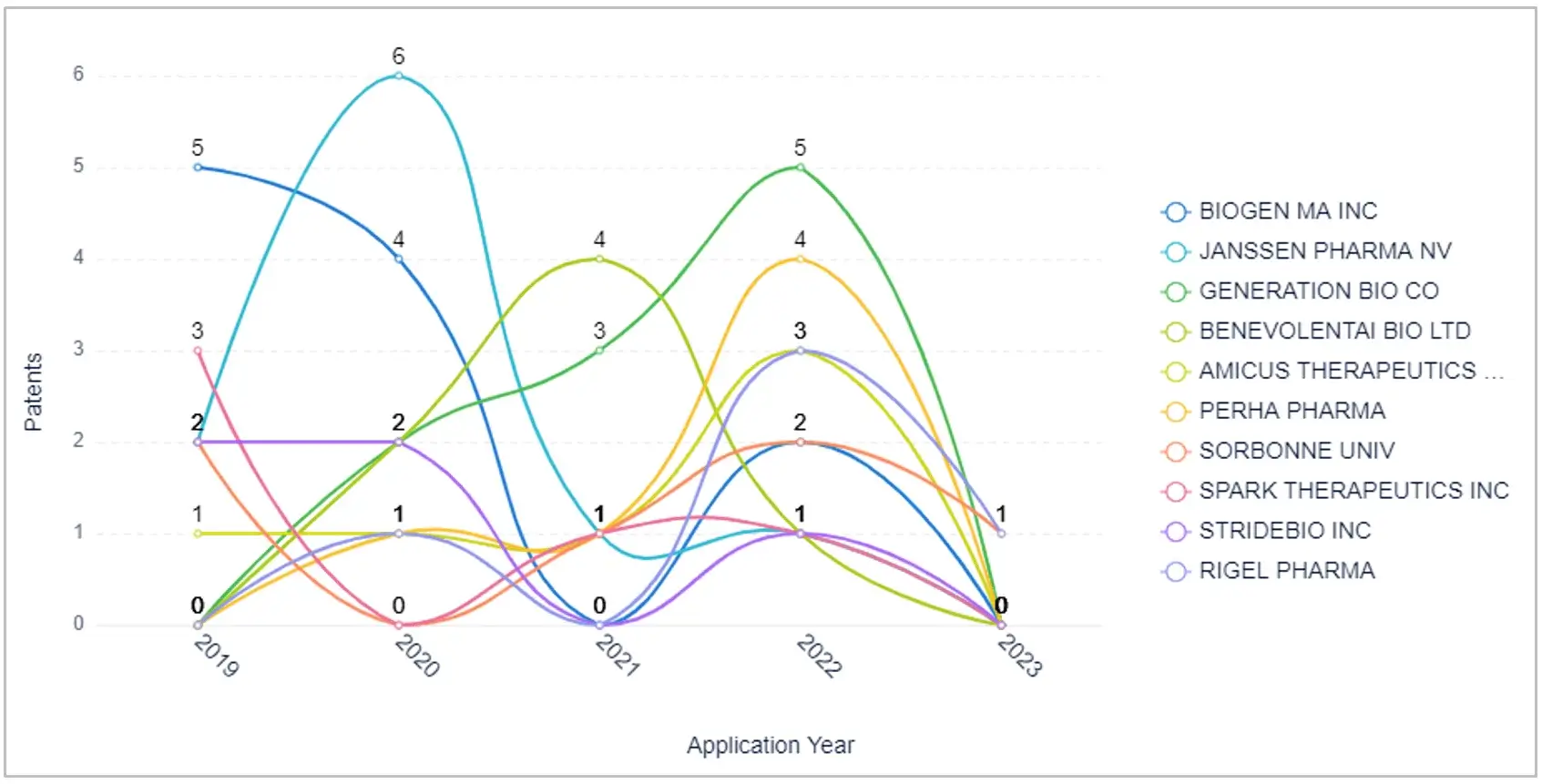
Data on the earliest application filed on the basis of the geographic source of the technology:
In the past five years, several drugs/therapies have undergone evaluation in registered clinical trials across various regions, progressing to later stages of development for Niemann-Pick Disease Type C (NPC).
Example illustration 1: Distribution of Clinical Trials by Status:
Example illustration 3: Distribution of Clinical Trials by Phase of Development:
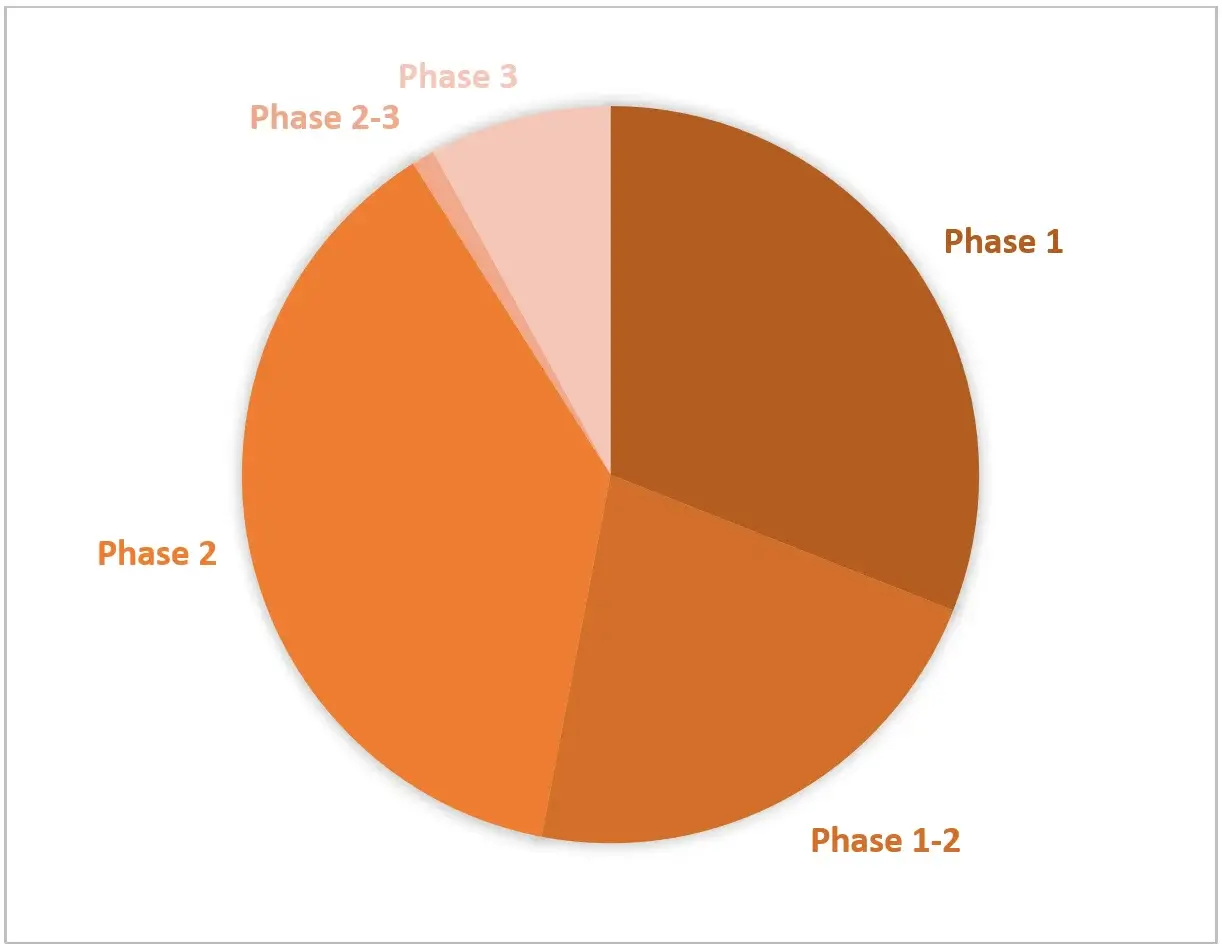
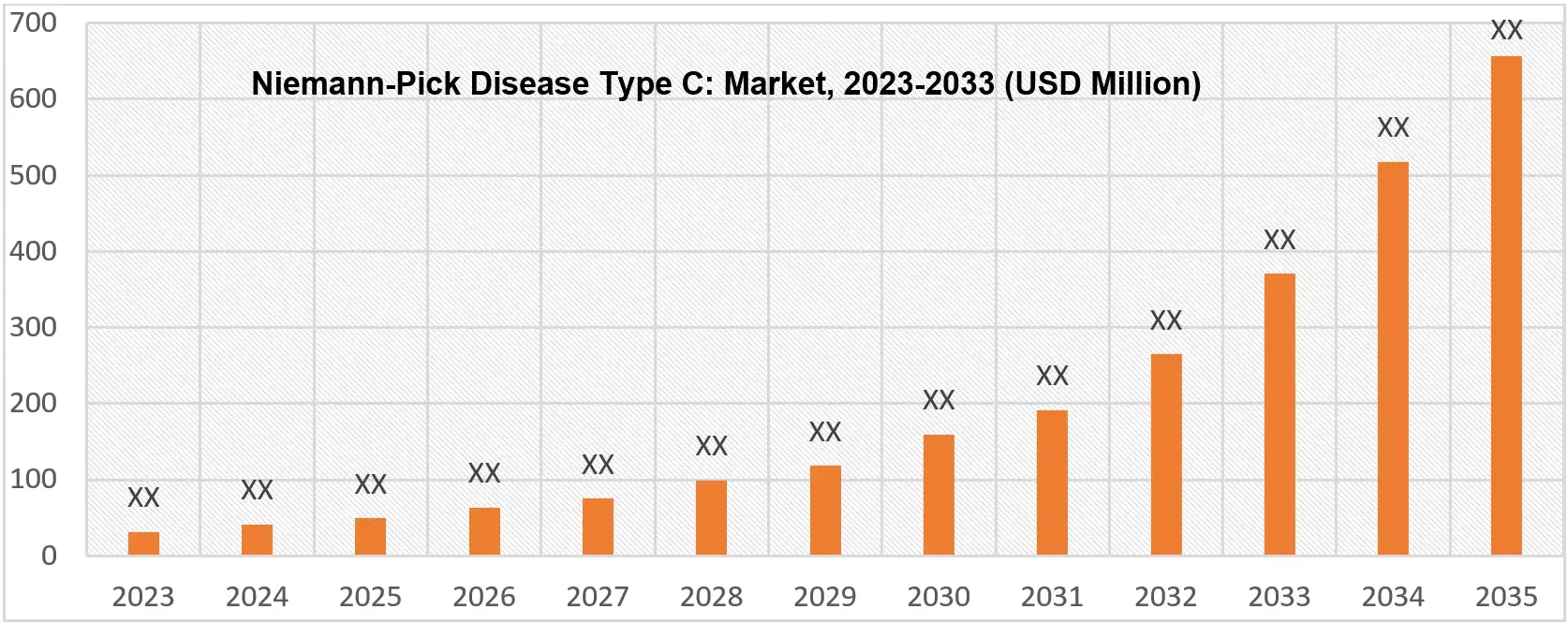
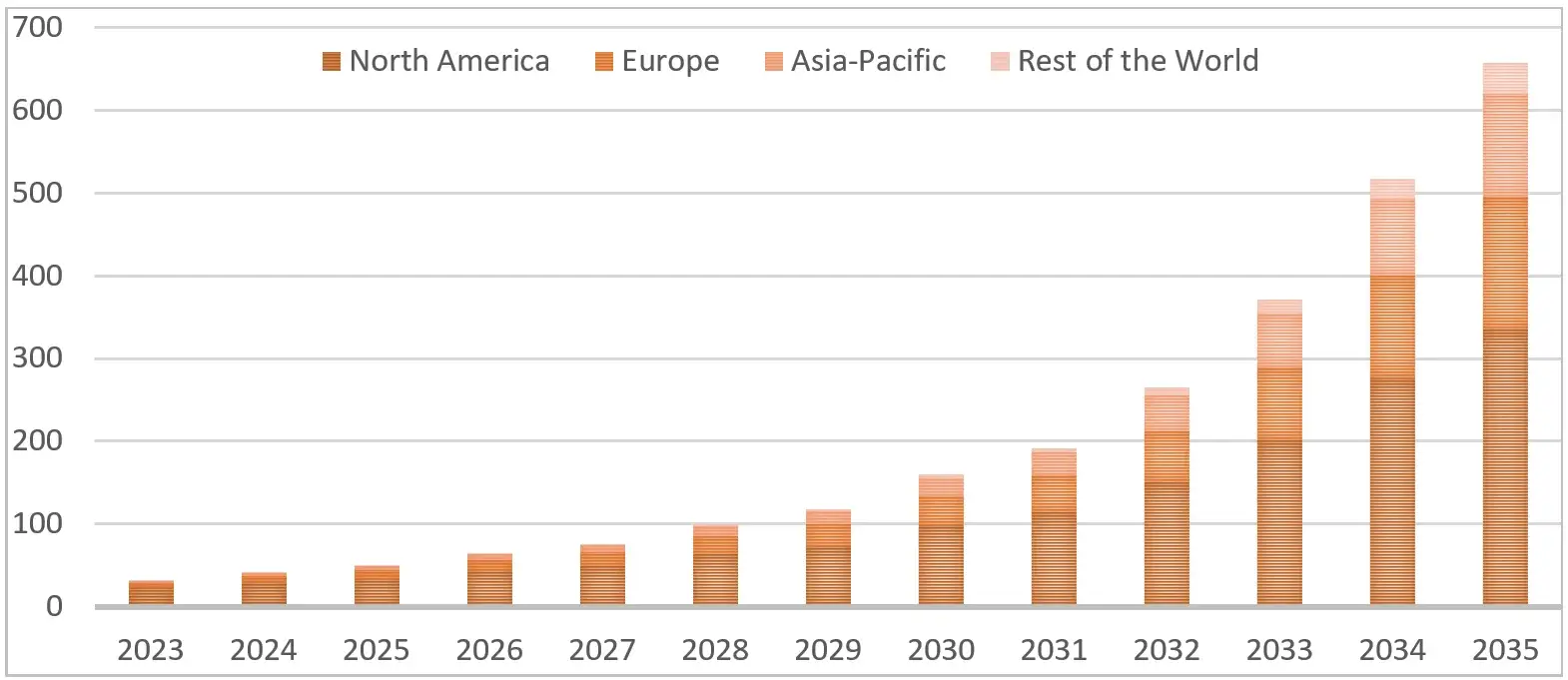
With endorsement for several promising drug candidates and observing encouraging clinical results, the Niemann-Pick Disease Type C (NPC) market is stratified into diverse segments, positioned for significant expansion in the forthcoming decade.
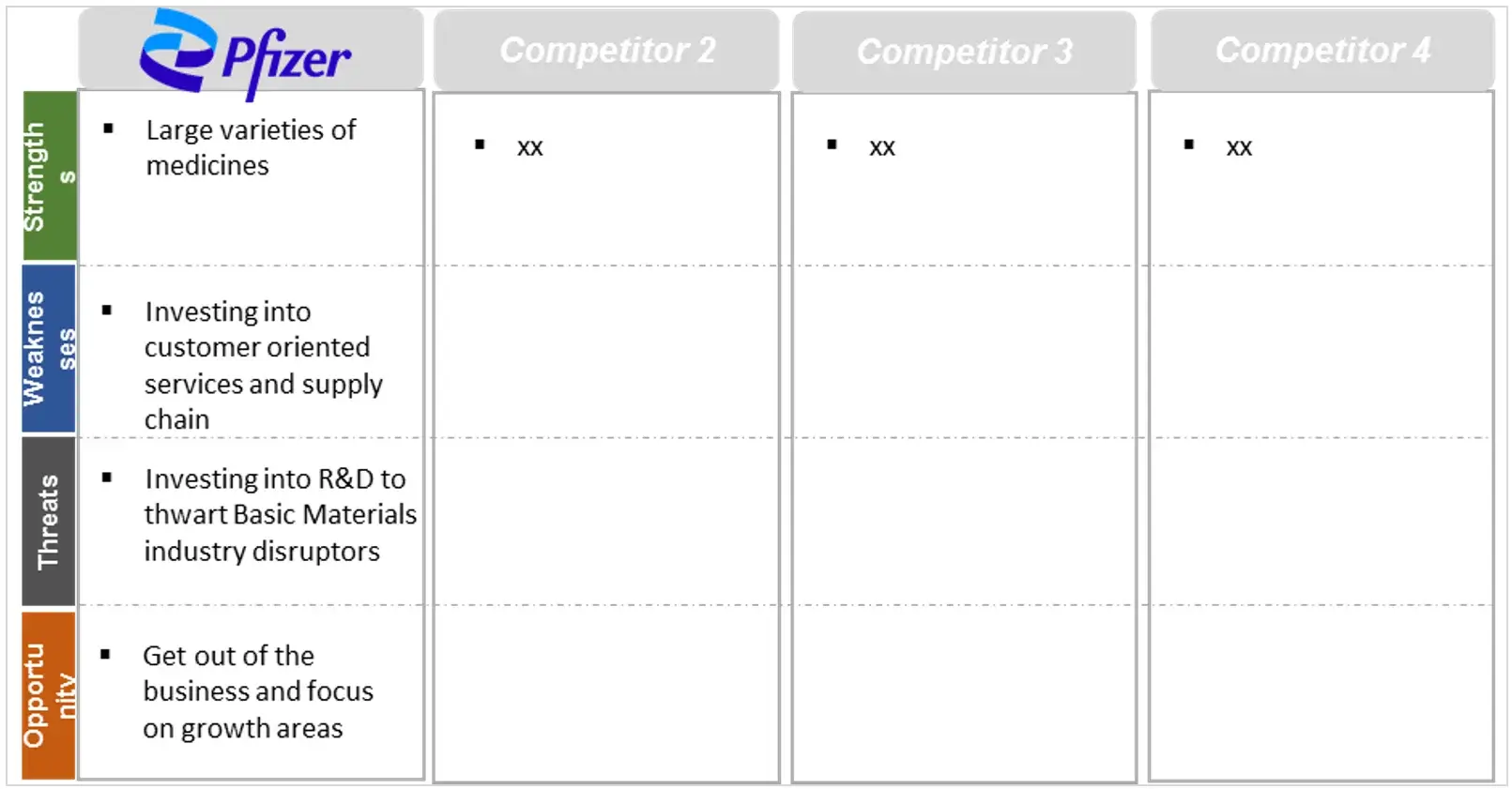
Considering the existence of multiple companies in the domain of Niemann-Pick Disease Type C (NPC), prospective contenders might arise in the market with aspirations to establish their prominence.
In order to give the most precise estimations and forecasts, Wissen Research uses an extensive and iterative research approach that is focused on reducing deviation. The company blends top-down and bottom-up methodologies for market segmentation and quantitative estimation. In addition, data triangulation, which examines the market from three separate angles, is a recurrent topic present in all of our research studies. Important components of the approach used for all of our studies include the following:
Preliminary data mining
On a wide scale, unprocessed market data is collected. Continuous data filtering makes sure that only verified and authenticated sources are taken into account. Additionally, data is extracted from a wide range of reports in our repository and from a number of reputable premium databases. We gather information from raw material suppliers, distributors, and purchasers to help with this since understanding the entire value chain is crucial for a thorough understanding of the market.
Surveys, technical symposia, and trade magazines are used to gather information on technical concerns and trends. Technical information focusing on white space and freedom of movement is also obtained from an intellectual property standpoint. Additionally, information on the industry’s drivers, constraints, and pricing patterns is obtained. As a result, a variety of original data are included in the material that is then cross-validated and certified with published sources.
Statistical model
We use simulation models to generate our market projections and estimates. Every study receives a special model that is tailored to it. Data for market dynamics, the technology environment, application development, and pricing patterns are gathered and supplied into the model all at once for analysis. The relative relevance of these factors is investigated, and their impact on the forecast period is assessed, using correlation, regression, and time series analysis. The process of market forecasting combines technological analysis with economic strategies, practical business acumen, and subject expertise.
Econometric models are frequently used for short-term forecasting, but technology market models are typically employed for long-term forecasting. These are based on a confluence of the business environment, regulatory environment, economic projection, and technical landscape. In order to develop global estimates, it is preferable to estimate markets from the bottom up by integrating data from key regional markets. This is required to ensure accuracy and a complete comprehension of the subject. Among the variables taken into account for forecasting are:
Regulations and anticipated developments
We give these criteria weights and use weighted average analysis to assess their market influence in order to calculate the anticipated market growth rate.
Primary research | Secondary research |
· Manufacturers · Technology distributors and wholesalers · End-user surveys · Consumer surveys | · Company reports and publications · Government publications · Independent investigations · Economic and demographic data · Online searches · Literature studies · Research reviews · Case studies · Reference customers |
1.1 Overview of Niemann-Pick Disease Type C (NPC)
1.1.1 Definition and Variants of NPC
1.1.2 Incidence and Prevalence of NPC
1.2 Epidemiology and Incidence Rates for NPC
1.2.1 NPC Incidence and Regional Variances
1.2.2 Prevalence across Age Groups and Geographical Regions for NPC
1.3 Symptoms and Diagnosis in NPC
1.3.1 Common Symptoms and Clinical Presentation of NPC
1.3.2 Diagnostic Methods, Biomarkers, and Imaging Techniques for NPC
1.4 Pathophysiology of NPC
1.4.1 Mechanisms Underlying Niemann-Pick Disease Type C
1.4.2 Gastrointestinal Implications and Progression of NPC
1.5 Causes and Risk Factors for NPC
1.5.1 Genetic and Environmental Influences in NPC
1.5.2 Factors Contributing to Disease Progression in NPC
2.1 Genetic Basis and Classification of NPC
2.1.1 Genetic Variants Associated with Niemann-Pick Disease Type C
2.1.2 Subtypes Classification of Niemann-Pick Disease Type C
2.2 Clinical Presentation and Disease Progression in NPC
2.2.1 Common Symptoms and Variability in Presentation of NPC
2.2.2 Disease Progression and Potential Complications in NPC
2.3 Diagnostic Tools and Approaches for NPC
2.3.1 Serological Testing and Genetic Markers in NPC
2.3.2 Endoscopy and Histological Assessment for NPC
2.4 Prognostic Factors and Natural History of NPC
2.4.1 Predictors of Disease Severity and Long-term Outcomes in NPC
2.4.2 Variability in Clinical Course and Disease Trajectory in NPC
3.1 Symptomatic Management of NPC
3.1.1 Dietary Modifications and Nutritional Guidance for NPC
3.1.2 Quality of Life Improvement and Symptom Management in NPC
3.2 Pharmacological Therapies for NPC
3.2.1 Enzyme Supplements and Medications for Symptom Relief in NPC
3.2.2 Emerging Drug Candidates and Potential Therapeutic Targets for NPC
3.3 Personalized Approaches for NPC
3.3.1 Genetic Testing and Customized Treatment Plans for NPC
3.3.2 Nutritional Counseling and Lifestyle Modifications for NPC
3.4 Investigational Therapies for NPC
3.4.1 Novel Therapeutic Modalities and Clinical Trials for NPC
3.4.2 Immune Modulation and Future Treatment Avenues for NPC
4.1 Global Niemann-Pick Disease Type C Market Overview
4.1.1 Market Size and Growth Trends for NPC
4.1.2 Regional Distribution and Patient Demographics in NPC
4.2 Market Trends and Innovations for NPC
4.2.1 Advancements in Diagnostics and Therapeutic Approaches for NPC
4.2.2 Digital Health Solutions and Patient Engagement in NPC
4.3 Market Drivers and Challenges for NPC
4.3.1 Regulatory Landscape and Labeling Regulations for NPC
4.3.2 Patient Education and Awareness Initiatives for NPC
5.1 Ongoing Clinical Trials and Investigational Studies for NPC
5.1.1 Pipeline Overview and Therapeutic Targets for NPC
5.1.2 Trial Progress and Patient Recruitment Status for NPC
5.2 Promising Therapies in Development for NPC
5.2.1 Emerging Drug Candidates and Mechanisms of Action for NPC
5.2.2 Potential Impact on Disease Management in NPC
5.3 Innovative Trial Designs and Endpoint Selection for NPC
5.3.1 Biomarkers and Patient-Centric Outcomes for NPC
5.3.2 Adaptive Trials and Real-World Evidence Integration for NPC
6.1 Leading Companies in Niemann-Pick Disease Type C Research and Therapeutics
6.1.1 Key Players and Market Share in NPC
6.1.2 Research and Development Initiatives in NPC
6.2 Company Profiles for NPC
6.2.1 Business Overview and Product Portfolios for NPC
6.2.2 Collaborations, Partnerships, and Licensing Activities for NPC
6.3 Market Dynamics and Competition for NPC
6.3.1 SWOT Analysis and Strategic Approaches for NPC
6.3.2 Market Entry Challenges and Future Outlook for NPC
7.1 Key Patents in Niemann-Pick Disease Type C Research
7.1.1 Notable Patents and Innovative Concepts for NPC
7.1.2 Intellectual Property Trends and Leading Innovators for NPC
7.2 Patent Analysis and Landscape Overview for NPC
7.2.1 Global Patent Trends and Filing Patterns for NPC
7.2.2 Patent Enforcement and Legal Considerations for NPC
8.1 Projected Growth and Market Forecast for NPC
8.1.1 Revenue Projections and Market Potential for NPC
8.1.2 Opportunities in Emerging Markets for NPC
8.2 Future Trends and Innovations for NPC
8.2.1 Precision Medicine and Personalized Treatment Plans for NPC
8.2.2 Technology-Enabled Disease Monitoring and Support for NPC
8.3 Patient-Centric Care and Enhancing Quality of Life for NPC
8.3.1 Patient Empowerment and Support Networks for NPC
8.3.2 Impact of Novel Therapeutic Modalities on Patient Experience in NPC
9.1 United States Market Size and Trends for NPC
9.1.1 Total Market Size of Niemann-Pick Disease Type C in the United States (2023-2033)
9.1.2 Treatment Landscape and Market Dynamics for NPC
9.2 European Market Size and Insights for NPC
9.2.1 Total Market Size of Niemann-Pick Disease Type C in Europe (2023-2033)
9.2.2 Market Trends and Treatment Patterns for NPC
9.3 Asia-Pacific Market Size and Assessment for NPC
9.3.1 Total Market Size of Niemann-Pick Disease Type C in Asia-Pacific (2023-2033)
9.3.2 Market Developments and Therapeutic Uptake for NPC
S.no | Key Highlights of Report | |
1. | Patent Analysis | · Top Assignee · Geography focus of top Assignees · Assignee Segmentation · Network analysis of the top collaborating entities in Niemann-Pick Disease Type C treatments patent applications · Technology Evolution · Key Patents · Application and Issued Trend · Key technology |
2. | Market analysis | · Current Treatment Options · Emerging Therapies and Research Developments (by product analysis and scientific analysis) · Strategic activities · Therapeutic activity of drugs · Company portfolio |
3. | Clinical Trials | · Analysis of clinical trial through graphical representation · Coverage of treatments from pre-clinical phases till commercialization (also including terminated and completed studies) |
4. | Forecast | · Detailed comprehension of the historic, current and forecasted trend of market by analysis of impact of these treatments on the market |
5. | Key Players | · Detailed profiles of the key players that are engaged in the development of approved drugs · Strategic Activities |
6. | Opportunity Analysis | · Technology evolution based on problem solution · Potential licensees · Geography of suppliers · Treatment trends · Unmet needs · SWOT · Drivers and barriers · Opportunity for new treatment |
7. | KOLs | · A detailed analysis and identification of the key opinion leaders (KOLs), shortlisted based on their contributions |
LIST OF FIGURES
Figure number | Description |
Figure 1 | Terminology of Niemann- Pick Disease Type C Over The Years |
Figure 2 | Niemann- Pick Disease Type C Treatment– History and Present |
Figure 3 | Projection of Niemann- Pick Disease Type C till 2033 in different geographies |
Figure 4 | Technology Categorization Of Drug Delivery Methods For Niemann- Pick Disease Type C |
Figure 5 | Recent Technology Trends in Niemann- Pick Disease Type C |
Figure 6 | Technology Evolution in Drug Delivery Market of Niemann- Pick Disease Type C |
Figure 7 | Geographical Distribution of Patents of Top Assignees |
Figure 8 | Assignee Segmentation (Companies) |
Figure 9 | Assignee Segmentation (Educational Establishment) |
Figure 10 | Patent Based Key Insights Of xx |
Figure 11 | Patent Based Key insights of xx |
Figure 12 | Patent Based Key insights of xx |
Figure 13 | Geographic Distribution of the Universities/Research Organizations Filling Patents On Various Drug Delivery Approaches |
Figure 14 | Key Summary Regarding the Patent Filing On Niemann- Pick Disease Type C |
Figure 15 | Product Pipeline of Different Approaches with Companies Name |
Figure 16 | Portfolio for Approved Product |
Figure 17 | Clinical Trials Conducted till Date by Different Companies and Universities |
Figure 18 | Clinical Trials based Key Insights |
Figure 19 | Key Growth Drivers for Niemann- Pick Disease Type C Market |
Figure 20 | Restraints for Niemann- Pick Disease Type C Market |
Figure 21 | xx Portfolio (Top Player) |
Figure 22 | xx Portfolio (Top Player) |
Figure 23 | xx Portfolio (Top Player) |
Figure 24 | xx Portfolio (Top Player) |
Figure 25 | xx Portfolio (Top Player) |
Figure 26 | xx Portfolio (Start-up) |
Figure 27 | xx Portfolio (Start-up) |
Figure 28 | xx Portfolio (Start-up) |
Figure 29 | Strategic Activities Including Collaboration, Partnerships and Acquisitions |
Figure 30 | Research Methodology for Patent, Selection and Analysis |
Figure 31 | Research Methodology for Scientific Literature, Selection and Analysis |
Figure 32 | Research Methodology for Clinical Trials, Selection and Analysis |
LIST OF GRAPHS
Graph number |
Description |
Graph 1 | Number of people worldwide with Niemann- Pick Disease Type C |
Graph 2 | Problem Solution Analysis |
Graph 3 | Top Assignees in Niemann- Pick Disease Type C |
Graph 4 | Technology Focus of Top Assignees (IPC-CPC Classes) |
Graph 5 | Top Countries of Origin of Patents |
Graph 6 | New entrants in drug delivery field |
Graph 7 | Legal Status |
Graph 8 | Most Cited Patents |
Graph 9 | Patents with Largest Invention Families |
Graph 10 | Most Claim-Heavy Patents |
Graph 11 | Filing Trends |
Graph 12 | Literature Filling Trend During Time Period (2018 – 2023) |
Graph 13 | Clinical Trial Filing Timeline |
Graph 14 | Recruitment Status of the Clinical Trials Related to the Different Drug Delivery Approaches |
Graph 15 | Clinical Trials Phases with Respect to Specific Drug Delivery Approach |
Graph 16 | Weighted Scores for Top 64 Players According to Benchmarking Criteria |
Graph 17 | Niemann- Pick Disease Type C (CAGR: 2023-2033) |
Graph 18 | Niemann- Pick Disease Type C Market Share: Distribution by Key Geographical Area, 2023-2033 |
LIST OF TABLES
Table number | Description |
Table 1 | Parameters included and excluded for conducting the analysis |
Table 2 | Technology Classes with Definitions |
Table 3 | Patent Litigation |
Table 4 | Highest Market Valued Patents |
Table 5 | SWOT Analysis of Top 3 Players |
Table 6 | Parameters and their score for Benchmarking |
Table 7 | Weighted scores for top 5 players according to benchmarking criteria |
Please Subscribe our news letter and get update.
© Copyright 2024 – Wissen Research All Rights Reserved.